Two Pointers¶
Table of Contents¶
- 283. Move Zeroes (Easy)
- 11. Container With Most Water (Medium)
- 15. 3Sum (Medium)
- 42. Trapping Rain Water (Hard)
283. Move Zeroes¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Easy)
-
Tags: array, two pointers
- Move all zeroes to the end of the array while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
283. Move Zeroes - Python Solution
from typing import List
def moveZeroes(nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
fast, slow = 0, 0
while fast < len(nums):
if nums[fast] != 0:
nums[slow], nums[fast] = nums[fast], nums[slow]
slow += 1
fast += 1
nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12]
moveZeroes(nums)
print(nums) # [1, 3, 12, 0, 0]
283. Move Zeroes - C++ Solution
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
size_t n = nums.size();
size_t fast = 0, slow = 0;
while (fast < n) {
if (nums[fast] != 0) {
swap(nums[slow], nums[fast]);
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {0, 1, 0, 3, 12};
moveZeroes(nums);
// [1, 3, 12, 0, 0]
for (size_t i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
11. Container With Most Water¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, two pointers, greedy
- Return the maximum area of water that can be trapped between the vertical lines.
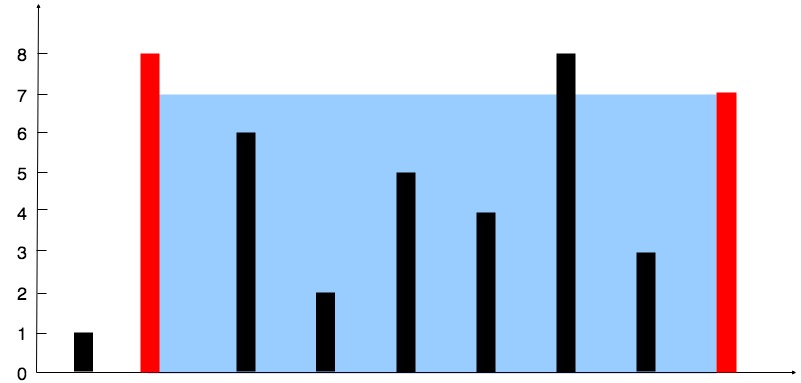
11. Container With Most Water - Python Solution
from typing import List
# Brute Force
def maxAreaBF(height: List[int]) -> int:
max_area = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(height)):
h = min(height[i], height[j])
w = j - i
max_area = max(max_area, h * w)
return max_area
# Left Right Pointers
def maxAreaLR(height: List[int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
res = 0
while left < right:
h = min(height[left], height[right])
w = right - left
res = max(res, h * w)
if height[left] < height[right]:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return res
# |------------|------- |---------|
# | Approach | Time | Space |
# |------------|--------|---------|
# | Brute Force| O(n^2) | O(1) |
# | Left Right | O(n) | O(1) |
# |------------|--------|---------|
height = [1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7]
print(maxAreaBF(height)) # 49
print(maxAreaLR(height)) # 49
11. Container With Most Water - C++ Solution
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int left = 0, right = height.size() - 1;
int res = 0;
while (left < right) {
int h = min(height[left], height[right]);
int w = right - left;
res = max(res, h * w);
if (height[left] < height[right])
left++;
else
right--;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
vector<int> height = {1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7};
cout << maxArea(height) << endl; // 49
return 0;
}
15. 3Sum¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, two pointers, sorting
15. 3Sum - Python Solution
from typing import List
# Left Right Pointers
def threeSum(nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
res = []
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n - 2):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
left, right = i + 1, n - 1
while left < right:
total = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]
if total > 0:
right -= 1
elif total < 0:
left += 1
else:
res.append([nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]])
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left + 1]:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] == nums[right - 1]:
right -= 1
left += 1
right -= 1
return res
nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
assert threeSum(nums) == [[-1, -1, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]
15. 3Sum - C++ Solution
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res;
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
int left = i + 1, right = n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int total = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (total > 0)
right--;
else if (total < 0)
left++;
else {
res.push_back({nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4};
vector<vector<int>> res = threeSum(nums);
for (auto& v : res) {
for (int i : v) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
42. Trapping Rain Water¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, two pointers, dynamic programming, stack, monotonic stack

| Approach | Time | Space |
|---|---|---|
| DP | O(N) | O(N) |
| Left Right | O(N) | O(1) |
| Monotonic | O(N) | O(N) |
42. Trapping Rain Water - Python Solution
from typing import List
# DP
def trapDP(height: List[int]) -> int:
if not height:
return 0
n = len(height)
maxLeft, maxRight = [0 for _ in range(n)], [0 for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(1, n):
maxLeft[i] = max(maxLeft[i - 1], height[i - 1])
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
maxRight[i] = max(maxRight[i + 1], height[i + 1])
res = 0
for i in range(n):
res += max(0, min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i])
return res
# Left Right Pointers
def trapLR(height: List[int]) -> int:
if not height:
return 0
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
maxL, maxR = height[left], height[right]
res = 0
while left < right:
if maxL < maxR:
left += 1
maxL = max(maxL, height[left])
res += maxL - height[left]
else:
right -= 1
maxR = max(maxR, height[right])
res += maxR - height[right]
return res
# Monotonic Stack
def trapStack(height: List[int]) -> int:
stack = []
total = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
while stack and height[i] > height[stack[-1]]:
top = stack.pop()
if not stack:
break
distance = i - stack[-1] - 1
bounded_height = min(height[i], height[stack[-1]]) - height[top]
total += distance * bounded_height
stack.append(i)
return total
height = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
print(trapDP(height)) # 6
print(trapLR(height)) # 6
print(trapStack(height)) # 6
42. Trapping Rain Water - C++ Solution
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int trap(vector<int> &height)
{
if (height.empty())
return 0;
int res = 0;
int left = 0, right = height.size() - 1;
int maxL = height[left], maxR = height[right];
while (left < right)
{
if (maxL < maxR)
{
left++;
maxL = max(maxL, height[left]);
res += maxL - height[left];
}
else
{
right--;
maxR = max(maxR, height[right]);
res += maxR - height[right];
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> height = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
Solution solution;
cout << solution.trap(height) << endl;
return 0;
}