Advanced Graphs¶
Table of Contents¶
- 332. Reconstruct Itinerary (Hard)
- 1584. Min Cost to Connect All Points (Medium)
- 743. Network Delay Time (Medium)
- 778. Swim in Rising Water (Hard)
- 269. Alien Dictionary (Hard) 👑
- 787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops (Medium)
332. Reconstruct Itinerary¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: depth first search, graph, eulerian circuit
- Return the itinerary in order that visits every airport exactly once.
- The starting airport is
JFK. - If there are multiple valid itineraries, return the lexicographically smallest one.
- Eulerian path: A path that visits every edge exactly once.
graph TD
JFK((JFK))
SFO((SFO))
ATL((ATL))
JFK --> SFO
SFO --> ATL
ATL --> JFK
JFK --> ATL
ATL --> SFO332. Reconstruct Itinerary - Python Solution
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Hierholzer
def findItinerary1(tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in sorted(tickets, reverse=True):
graph[u].append(v)
route = []
def dfs(node):
while graph[node]:
dest = graph[node].pop()
dfs(dest)
route.append(node)
dfs("JFK")
return route[::-1]
# Backtracking
def findItinerary2(tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = defaultdict(list)
tickets.sort()
for u, v in tickets:
graph[u].append(v)
route = ["JFK"]
def backtraking(node):
if len(route) == len(tickets) + 1:
return True
if node not in graph:
return False
temp = list(graph[node])
for i, v in enumerate(temp):
graph[node].pop(i)
route.append(v)
if backtraking(v):
return True
graph[node].insert(i, v)
route.pop()
return False
backtraking("JFK")
return route
tickets = tickets = [
["JFK", "SFO"],
["JFK", "ATL"],
["SFO", "ATL"],
["ATL", "JFK"],
["ATL", "SFO"],
]
print(findItinerary1(tickets))
# ['JFK', 'ATL', 'JFK', 'SFO', 'ATL', 'SFO']
print(findItinerary2(tickets))
# ['JFK', 'ATL', 'JFK', 'SFO', 'ATL', 'SFO']
1584. Min Cost to Connect All Points¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, union find, graph, minimum spanning tree
- Tree: a connected acyclic graph
- Spanning Tree: a subgraph that is a tree and connects all the vertices together
- Minimum Spanning Tree (MST): a spanning tree with the minimum possible sum of edge weights
- Prim's Algorithm
- Data Structure: Heap
- Time Complexity: O(E * logV)
- Space Complexity: O(V + E)
- Kruskal's Algorithm
- Union Find
- Time Complexity: O(E * logV)
- Space Complexity: O(V + E)
1584. Min Cost to Connect All Points - Python Solution
import heapq
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Prim
def minCostConnectPointsPrim(points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(points)
graph = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
x1, y1 = points[i]
x2, y2 = points[j]
dist = abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2)
graph[i].append((dist, j))
graph[j].append((dist, i))
cost = 0
heap = [(0, 0)] # (cost, node)
visited = set()
while heap:
d1, n1 = heapq.heappop(heap)
if n1 in visited:
continue
visited.add(n1)
cost += d1
for d2, n2 in graph[n1]:
if n2 not in visited:
heapq.heappush(heap, (d2, n2))
return cost
# Kruskal
def minCostConnectPointsKruskal(points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(points)
par = {i: i for i in range(n)}
rank = {i: 0 for i in range(n)}
def find(n):
p = par[n]
while p != par[p]:
par[p] = par[par[p]]
p = par[p]
return p
def union(n1, n2):
p1, p2 = find(n1), find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return False
if rank[p1] > rank[p2]:
par[p2] = p1
elif rank[p1] < rank[p2]:
par[p1] = p2
else:
par[p2] = p1
rank[p1] += 1
return True
heap = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
x1, y1 = points[i]
x2, y2 = points[j]
dist = abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2)
heapq.heappush(heap, (dist, i, j))
cost = 0
while heap:
d, n1, n2 = heapq.heappop(heap)
if union(n1, n2):
cost += d
return cost
if __name__ == "__main__":
points = [[0, 0], [2, 2], [3, 10], [5, 2], [7, 0]]
print(minCostConnectPointsPrim(points)) # 20
print(minCostConnectPointsKruskal(points)) # 20
743. Network Delay Time¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, heap priority queue, shortest path
- Return the minimum time taken to reach all nodes in a network.
graph LR
1((1))
2((2))
3((3))
4((4))
2 --> |1| 1
2 --> |1| 3
3 --> |1| 4- Shortest Path Problem: Find the shortest path between two vertices in a graph.
- Dijkstra's Algorithm
- Shortest path algorithm
- Weighted graph (non-negative weights)
- Data Structure: Heap; Hash Set
- Time Complexity: O(E * logV)
- Space Complexity: O(V)
743. Network Delay Time - Python Solution
import heapq
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Dijkstra - Set
def networkDelayTime1(times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in times:
graph[u].append((v, w))
heap = [(0, k)]
visit = set()
t = 0
while heap:
w1, n1 = heapq.heappop(heap)
if n1 in visit:
continue
visit.add(n1)
t = w1
for n2, w2 in graph[n1]:
heapq.heappush(heap, (w1 + w2, n2))
return t if len(visit) == n else -1
# Dijkstra - Dict
def networkDelayTime2(times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in times:
graph[u].append((v, w))
heap = [(0, k)]
dist = defaultdict(int)
while heap:
w1, n1 = heapq.heappop(heap)
if n1 in dist:
continue
dist[n1] = w1
for n2, w2 in graph[n1]:
heapq.heappush(heap, (w1 + w2, n2))
return max(dist.values()) if len(dist) == n else -1
# Bellman-Ford
def networkDelayTimeBF(times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
delay = {i: float("inf") for i in range(1, n + 1)}
delay[k] = 0
for _ in range(n - 1):
for u, v, t in times:
delay[v] = min(delay[v], delay[u] + t)
max_delay = max(delay.values())
return max_delay if max_delay < float("inf") else -1
# |--------------|-----------|--------|
# | Approach | Time | Space |
# |--------------|-----------|--------|
# | Dijkstra | O(E*logV) | O(V+E) |
# | Bellman-Ford | O(E*V) | O(V) |
# |--------------|-----------|--------|
if __name__ == "__main__":
times = [[2, 1, 1], [2, 3, 1], [3, 4, 1]]
n = 4
k = 2
print(networkDelayTime1(times, n, k)) # 2
print(networkDelayTime2(times, n, k)) # 2
print(networkDelayTimeBF(times, n, k)) # 2
778. Swim in Rising Water¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, binary search, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, heap priority queue, matrix
- Return the minimum time when you can reach the target.
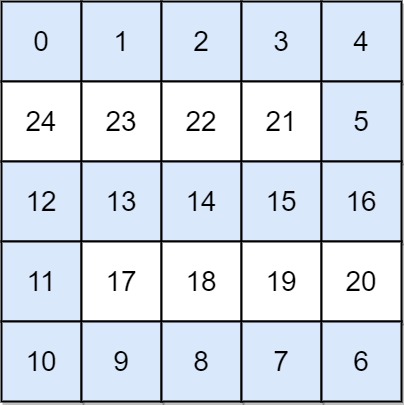
778. Swim in Rising Water - Python Solution
import heapq
from typing import List
# Dijkstra's
def swimInWater(grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
visited = set()
minHeap = [(grid[0][0], 0, 0)]
directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
visited.add((0, 0))
while minHeap:
time, r, c = heapq.heappop(minHeap)
if r == n - 1 and c == n - 1:
return time
for dr, dc in directions:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if nr in range(n) and nc in range(n) and (nr, nc) not in visited:
visited.add((nr, nc))
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (max(time, grid[nr][nc]), nr, nc))
grid = [
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[24, 23, 22, 21, 5],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16],
[11, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6],
]
print(swimInWater(grid)) # 16
269. Alien Dictionary¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, string, depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
- Return the correct order of characters in the alien language.
269. Alien Dictionary - Python Solution
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS - Kahn's algorithm (Topological Sort)
def alienOrderBFS(words: List[str]) -> str:
graph = defaultdict(set)
indegree = {c: 0 for word in words for c in word}
for i in range(len(words) - 1):
w1, w2 = words[i], words[i + 1]
minLen = min(len(w1), len(w2))
if len(w1) > len(w2) and w1[:minLen] == w2[:minLen]:
return ""
for j in range(minLen):
if w1[j] != w2[j]:
if w2[j] not in graph[w1[j]]:
graph[w1[j]].add(w2[j])
indegree[w2[j]] += 1
break
q = deque([c for c in indegree if indegree[c] == 0])
result = []
while q:
char = q.popleft()
result.append(char)
for neighbor in graph[char]:
indegree[neighbor] -= 1
if indegree[neighbor] == 0:
q.append(neighbor)
return "".join(result) if len(result) == len(indegree) else ""
# DFS - Topological Sort
def alienOrderDFS(words: List[str]) -> str:
graph = defaultdict(set)
visited = {}
result = []
for i in range(len(words) - 1):
w1, w2 = words[i], words[i + 1]
minLen = min(len(w1), len(w2))
if len(w1) > len(w2) and w1[:minLen] == w2[:minLen]:
return ""
for j in range(minLen):
if w1[j] != w2[j]:
if w2[j] not in graph[w1[j]]:
graph[w1[j]].add(w2[j])
break
def dfs(c):
if c in visited:
return visited[c]
visited[c] = False
for neighbor in graph[c]:
if not dfs(neighbor):
return False
visited[c] = True
result.append(c)
return True
for c in list(graph.keys()):
if not dfs(c):
return ""
return "".join(result[::-1])
words = ["wrt", "wrf", "er", "ett", "rftt"]
print(alienOrderBFS(words)) # wertf
print(alienOrderDFS(words)) # wertf
787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: dynamic programming, depth first search, breadth first search, graph, heap priority queue, shortest path
- Return the cheapest price from
srctodstwith at mostKstops.
graph TD
0((0))
1((1))
2((2))
3((3))
0 --> |100| 1
1 --> |600| 3
1 --> |100| 2
2 --> |100| 0
2 --> |200| 3787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops - Python Solution
import heapq
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Bellman-Ford
def findCheapestPriceBF(
n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int
) -> int:
prices = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
prices[src] = 0
for _ in range(k + 1):
temp = prices[:]
for u, v, w in flights:
temp[v] = min(temp[v], prices[u] + w)
prices = temp
return prices[dst] if prices[dst] != float("inf") else -1
# Dijkstra
def findCheapestPriceDijkstra(
n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int
) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in flights:
graph[u].append((v, w))
heap = [(0, src, 0)] # (price, city, stops)
visited = defaultdict(int) # {city: stops}
while heap:
price, city, stops = heapq.heappop(heap)
if city == dst:
return price
if stops > k:
continue
if city in visited and visited[city] <= stops:
continue
visited[city] = stops
for neighbor, cost in graph[city]:
heapq.heappush(heap, (price + cost, neighbor, stops + 1))
return -1
# |------------|------------------|---------|
# | Approach | Time | Space |
# |------------|------------------|---------|
# |Bellman-Ford| O(k * E) | O(n) |
# | Dijkstra | O(E * log(V)) | O(n) |
# |------------|------------------|---------|
n = 4
flights = [[0, 1, 100], [1, 2, 100], [2, 0, 100], [1, 3, 600], [2, 3, 200]]
src = 0
dst = 3
k = 1
print(findCheapestPriceBF(n, flights, src, dst, k)) # 700
print(findCheapestPriceDijkstra(n, flights, src, dst, k)) # 700