Graph BFS¶
Table of Contents¶
- 994. Rotting Oranges (Medium)
- 127. Word Ladder (Hard)
- 1466. Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero (Medium)
- 286. Walls and Gates (Medium) 👑
- 815. Bus Routes (Hard)
994. Rotting Oranges¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, breadth first search, matrix
- Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange.
- Hint: Multi-source BFS to count the level.
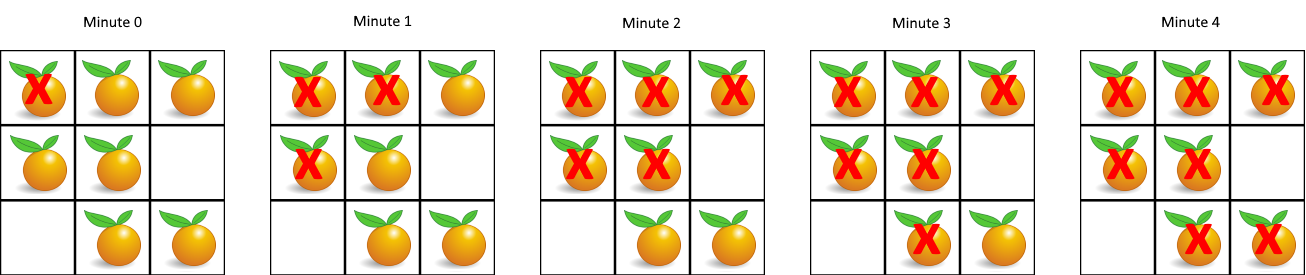
994. Rotting Oranges - Python Solution
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def orangesRotting(grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
fresh = 0
q = deque()
dirs = [[1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 2:
q.append([i, j])
elif grid[i][j] == 1:
fresh += 1
res = 0
while q and fresh > 0:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
r, c = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = dr + r, dc + c
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and grid[nr][nc] == 1:
q.append([nr, nc])
grid[nr][nc] = 2
fresh -= 1
res += 1
return res if fresh == 0 else -1
grid = [[2, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1]]
assert orangesRotting(grid) == 4
127. Word Ladder¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: hash table, string, breadth first search
- The most classic BFS problem.
- Return the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, or 0 if no such sequence exists.
- Approach: BFS
- Time Complexity: O(n * m^2)
- Space Complexity: O(n * m)
127. Word Ladder - Python Solution
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def ladderLength(beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
n = len(beginWord)
graph = defaultdict(list) # pattern: words
wordList.append(beginWord)
for word in wordList:
for i in range(n):
pattern = word[:i] + "*" + word[i + 1 :]
graph[pattern].append(word)
visited = set([beginWord])
q = deque([beginWord])
res = 1
while q:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
word = q.popleft()
if word == endWord:
return res
for i in range(n):
pattern = word[:i] + "*" + word[i + 1 :]
for neighbor in graph[pattern]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor)
q.append(neighbor)
res += 1
return 0
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"]
print(ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList)) # 5
1466. Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph
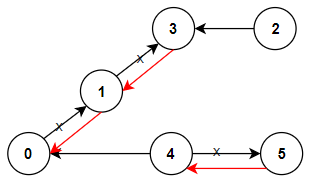
1466. Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero - Python Solution
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def minReorderBFS(n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in connections:
graph[u].append((v, 1)) # go
graph[v].append((u, 0)) # come
changes = 0
q = deque([(0, -1)])
while q:
n1, d1 = q.popleft()
for n2, d2 in graph[n1]:
if n2 != d1:
changes += d2
q.append((n2, n1))
return changes
# DFS
def minReorderDFS(n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in connections:
graph[u].append((v, 1)) # go
graph[v].append((u, 0)) # come
def dfs(n1, d1):
changes = 0
for n2, d2 in graph[n1]:
if n2 != d1:
changes += d2 + dfs(n2, n1)
return changes
return dfs(0, -1)
n = 5
connections = [[1, 0], [1, 2], [3, 2], [3, 4]]
print(minReorderBFS(n, connections)) # 2
print(minReorderDFS(n, connections)) # 2
286. Walls and Gates¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, breadth first search, matrix
286. Walls and Gates - Python Solution
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# Multi-Source BFS
def wallsAndGates(rooms: List[List[int]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify rooms in-place instead.
"""
m, n = len(rooms), len(rooms[0])
visited = set()
directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
def addRoom(r, c):
if (
0 <= r < m
and 0 <= c < n
and (r, c) not in visited
and rooms[r][c] != -1
):
q.append((r, c))
visited.add((r, c))
q = deque()
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if rooms[r][c] == 0:
q.append((r, c))
visited.add((r, c))
dist = 0
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
r, c = q.popleft()
rooms[r][c] = dist
for dr, dc in directions:
addRoom(r + dr, c + dc)
dist += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
rooms = [
[2147483647, -1, 0, 2147483647],
[2147483647, 2147483647, 2147483647, -1],
[2147483647, -1, 2147483647, -1],
[0, -1, 2147483647, 2147483647],
]
wallsAndGates(rooms)
assert rooms == [
[3, -1, 0, 1],
[2, 2, 1, -1],
[1, -1, 2, -1],
[0, -1, 3, 4],
]
815. Bus Routes¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, hash table, breadth first search
815. Bus Routes - Python Solution
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def numBusesToDestination(
routes: List[List[int]], source: int, target: int
) -> int:
if source == target:
return 0
graph = defaultdict(set) # {stop: buses}
for buses, route in enumerate(routes):
for stop in route:
graph[stop].add(buses)
q = deque([(source, 0)]) # (stop, bus)
visited_stops = set([source])
visited_buses = set()
while q:
stop, bus = q.popleft()
if stop == target:
return bus
for buses in graph[stop]:
if buses not in visited_buses:
visited_buses.add(buses)
for next_stop in routes[buses]:
if next_stop not in visited_stops:
visited_stops.add(next_stop)
q.append((next_stop, bus + 1))
return -1
routes = [[1, 2, 7], [3, 6, 7]]
source = 1
target = 6
print(numBusesToDestination(routes, source, target)) # 2