Graph¶
Table of Contents¶
- 200. Number of Islands (Medium)
- 130. Surrounded Regions (Medium)
- 133. Clone Graph (Medium)
- 399. Evaluate Division (Medium)
- 207. Course Schedule (Medium)
- 210. Course Schedule II (Medium)
200. Number of Islands¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, matrix
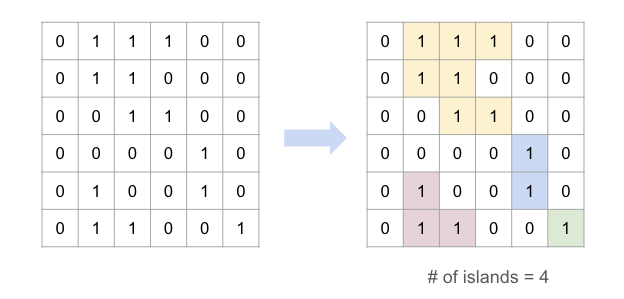
- Count the number of islands in a 2D grid.
- Method 1: DFS
-
Method 2: BFS (use a queue to traverse the grid)
-
How to keep track of visited cells?
- Mark the visited cell as
0(or any other value) to avoid revisiting it. - Use a set to store the visited cells.
- Mark the visited cell as
-
Steps:
- Init: variables
- DFS/BFS: starting from the cell with
1, turn all the connected1s to0. - Traverse the grid, and if the cell is
1, increment the count and call DFS/BFS.
from collections import deque
from copy import deepcopy
from typing import List
# DFS
def numIslandsDFS(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
res = 0
def dfs(r, c):
if r < 0 or r >= m or c < 0 or c >= n or grid[r][c] != "1":
return
grid[r][c] = "2"
dfs(r + 1, c)
dfs(r - 1, c)
dfs(r, c + 1)
dfs(r, c - 1)
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == "1":
dfs(r, c)
res += 1
return res
# BFS + Set
def numIslandsBFS1(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
visited = set()
res = 0
def bfs(r, c):
q = deque([(r, c)])
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = row + dr, col + dc
if (
nr < 0
or nr >= m
or nc < 0
or nc >= n
or grid[nr][nc] == "0"
or (nr, nc) in visited
):
continue
visited.add((nr, nc))
q.append((nr, nc))
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == "1" and (r, c) not in visited:
visited.add((r, c))
bfs(r, c)
res += 1
return res
# BFS + Grid
def numIslandsBFS2(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]
res = 0
def bfs(r, c):
q = deque([(r, c)])
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = dr + row, dc + col
if (
nr < 0
or nr >= m
or nc < 0
or nc >= n
or grid[nr][nc] != "1"
):
continue
grid[nr][nc] = "2"
q.append((nr, nc))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == "1":
grid[i][j] = "2"
bfs(i, j)
res += 1
return res
grid = [
["1", "1", "1", "1", "0"],
["1", "1", "0", "1", "0"],
["1", "1", "0", "0", "0"],
["0", "0", "0", "0", "0"],
]
print(numIslandsDFS(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
print(numIslandsBFS1(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
print(numIslandsBFS2(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
private:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int r, int c)
{
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
if (r < 0 || r >= row || c < 0 || c >= col || grid[r][c] != '1')
{
return;
}
grid[r][c] = '0';
dfs(grid, r - 1, c);
dfs(grid, r + 1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c - 1);
dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1')
{
res++;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> grid = {
{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
{'0', '0', '1', '0', '0'},
{'0', '0', '0', '1', '1'}};
cout << s.numIslands(grid) << endl;
return 0;
}
130. Surrounded Regions¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, matrix
from collections import deque
from copy import deepcopy
from typing import List
# DFS
def solveDFS(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board and not board[0]:
return None
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
def capture(r, c):
if r < 0 or r >= m or c < 0 or c >= n or board[r][c] != "O":
return None
board[r][c] = "T"
capture(r + 1, c)
capture(r - 1, c)
capture(r, c + 1)
capture(r, c - 1)
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "O" and (r in [0, m - 1] or c in [0, n - 1]):
capture(r, c)
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "O":
board[r][c] = "X"
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "T":
board[r][c] = "O"
# BFS
def solveBFS(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board and not board[0]:
return None
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
dirs = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
def capture(r, c):
q = deque([(r, c)])
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr = row + dr
nc = col + dc
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and board[nr][nc] == "O":
board[nr][nc] = "T"
q.append((nr, nc))
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "O" and (r in [0, m - 1] or c in [0, n - 1]):
board[r][c] = "T"
capture(r, c)
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "O":
board[r][c] = "X"
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if board[r][c] == "T":
board[r][c] = "O"
if __name__ == "__main__":
board = [
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "O", "O", "X"],
["X", "X", "O", "X"],
["X", "O", "X", "X"],
]
b = deepcopy(board)
solveDFS(b)
assert b == [
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "O", "X", "X"],
]
b = deepcopy(board)
solveBFS(b)
assert b == [
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "X", "X", "X"],
["X", "O", "X", "X"],
]
133. Clone Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: hash table, depth first search, breadth first search, graph
from collections import deque
from typing import Optional
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=0, neighbors=None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
# 1. DFS
def cloneGraphDFS(node: Optional["Node"]) -> Optional["Node"]:
if not node:
return None
cloned = {} # {old: new}
def dfs(node):
if node in cloned:
return cloned[node]
new = Node(node.val)
cloned[node] = new
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
new.neighbors.append(dfs(neighbor))
return new
return dfs(node)
# 2. BFS
def cloneGraphBFS(node: Optional["Node"]) -> Optional["Node"]:
if not node:
return None
cloned = {node: Node(node.val)}
q = deque([node])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for neighbor in cur.neighbors:
if neighbor not in cloned:
cloned[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val)
q.append(neighbor)
cloned[cur].neighbors.append(cloned[neighbor])
return cloned[node]
399. Evaluate Division¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, string, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph, shortest path
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Union Find
def calcEquation(
equations: List[List[str]], values: List[float], queries: List[List[str]]
) -> List[float]:
graph = defaultdict(dict)
for (a, b), v in zip(equations, values):
graph[a][b] = v
graph[b][a] = 1 / v
def dfs(a, b, visited):
if a not in graph or b not in graph:
return -1.0
if b in graph[a]:
return graph[a][b]
for c in graph[a]:
if c not in visited:
visited.add(c)
d = dfs(c, b, visited)
if d != -1.0:
return graph[a][c] * d
return -1.0
result = []
for a, b in queries:
result.append(dfs(a, b, set()))
return result
equations = [["a", "b"], ["b", "c"]]
values = [2.0, 3.0]
queries = [["a", "c"], ["b", "a"], ["a", "e"], ["a", "a"], ["x", "x"]]
print(calcEquation(equations, values, queries)) # [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0]
207. Course Schedule¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
- Return true if it is possible to finish all courses, otherwise return false.
- Dependency relationships imply the topological sort algorithm.
- Cycle detection
- Topological Sort
- DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- Time complexity: O(V+E)
- Space complexity: O(V+E)
- Prerequisites: Indegree (Look at the problem 1557. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes)
- Indegree: Number of incoming edges to a vertex
- Applications: task scheduling, course scheduling, build systems, dependency resolution, compiler optimization, etc.
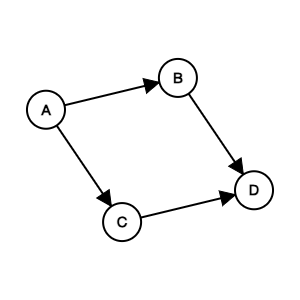
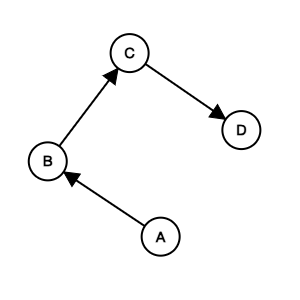
Course to prerequisites mapping
flowchart LR
0((0)) --> 1((1))
0((0)) --> 2((2))
1((1)) --> 3((3))
3((3)) --> 4((4))
1((1)) --> 4((4))Prerequisites to course mapping
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
2((2)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| course | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Initialize
- graph
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| course | [0] |
[0] |
[1] |
[1, 3] |
- in-degree
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[2, 4] - pop
2from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[4] - pop
4from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[3] - pop
3from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[1] - pop
1from the queue
flowchart LR
0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[0] - pop
0from the queue - All courses are taken. Return
True.
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS (Kahn's Algorithm)
def canFinishBFS(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[pre].append(crs)
indegree[crs] += 1
q = deque([i for i in range(numCourses) if indegree[i] == 0])
count = 0
while q:
crs = q.popleft()
count += 1
for nxt in graph[crs]:
indegree[nxt] -= 1
if indegree[nxt] == 0:
q.append(nxt)
return count == numCourses
# DFS + Set
def canFinishDFS1(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
visiting = set()
def dfs(crs):
if crs in visiting: # cycle detected
return False
if graph[crs] == []:
return True
visiting.add(crs)
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
visiting.remove(crs)
graph[crs] = []
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
# DFS + List
def canFinishDFS2(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for pre, crs in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
# 0: init, 1: visiting, 2: visited
status = [0] * numCourses
def dfs(crs):
if status[crs] == 1: # cycle detected
return False
if status[crs] == 2:
return True
status[crs] = 1
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
status[crs] = 2
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
prerequisites = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [3, 4]]
print(canFinishBFS(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS1(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS2(5, prerequisites)) # True
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// BFS
bool canFinishBFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
indegree[pre[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
cnt++;
for (int nxt : graph[cur]) {
indegree[nxt]--;
if (indegree[nxt] == 0) {
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
return cnt == numCourses;
}
// DFS
bool canFinishDFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
}
// 0: not visited, 1: visiting, 2: visited
vector<int> state(numCourses, 0);
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int pre) -> bool {
state[pre] = 1; // visiting
for (int crs : graph[pre]) {
if (state[crs] == 1 || (state[crs] == 0 && dfs(crs))) {
return true;
}
}
state[pre] = 2; // visited
return false;
};
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (state[i] == 0 && dfs(i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Solution sol;
vector<vector<int>> prerequisites = {{1, 0}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3},
{5, 4}, {6, 5}, {7, 6}, {8, 7},
{9, 8}, {10, 9}};
int numCourses = 11;
cout << sol.canFinishBFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
cout << sol.canFinishDFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
return 0;
}
210. Course Schedule II¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
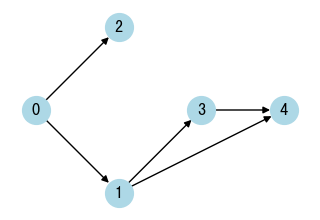
- Return the ordering of courses you should take to finish all courses. If there are multiple valid answers, return any of them.
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# 1. BFS - Kahn's Algorithm
def findOrderBFS(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[pre].append(crs)
indegree[crs] += 1
q = deque([i for i in range(numCourses) if indegree[i] == 0])
order = []
while q:
pre = q.popleft()
order.append(pre)
for crs in graph[pre]:
indegree[crs] -= 1
if indegree[crs] == 0:
q.append(crs)
return order if len(order) == numCourses else []
# 2. DFS + Set
def findOrderDFS1(
numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]
) -> List[int]:
adj = defaultdict(list)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
adj[crs].append(pre)
visit, cycle = set(), set()
order = []
def dfs(crs):
if crs in cycle:
return False
if crs in visit:
return True
cycle.add(crs)
for pre in adj[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
cycle.remove(crs)
visit.add(crs)
order.append(crs)
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return []
return order
# 3. DFS + List
def findOrderDFS2(
numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]
) -> List[int]:
adj = defaultdict(list)
for pre, crs in prerequisites:
adj[crs].append(pre)
# 0: not visited, 1: visiting, 2: visited
state = [0] * numCourses
order = []
def dfs(crs):
if state[crs] == 1:
return False
if state[crs] == 2:
return True
state[crs] = 1
for pre in adj[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
state[crs] = 2
order.append(crs)
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return []
return order[::-1]
numCourses = 5
prerequisites = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [3, 4]]
print(findOrderBFS(numCourses, prerequisites)) # [2, 4, 3, 1, 0]
print(findOrderDFS1(numCourses, prerequisites)) # [4, 3, 1, 2, 0]
print(findOrderDFS2(numCourses, prerequisites)) # [4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// BFS
vector<int> findOrderBFS(int numCourses,
vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
indegree[pre[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++)
if (indegree[i] == 0) q.push(i);
vector<int> order;
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
order.push_back(cur);
for (int nxt : graph[cur]) {
indegree[nxt]--;
if (indegree[nxt] == 0) q.push(nxt);
}
}
return (int)order.size() == numCourses ? order : vector<int>{};
}
};
int main() {
Solution obj;
vector<vector<int>> prerequisites{{1, 0}, {2, 0}, {3, 1}, {3, 2}};
vector<int> res = obj.findOrderBFS(4, prerequisites);
for (size_t i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) cout << res[i] << "\n";
return 0;
}