Graph¶
Table of Contents¶
- 733. Flood Fill (Easy)
- 542. 01 Matrix (Medium)
- 133. Clone Graph (Medium)
- 207. Course Schedule (Medium)
- 200. Number of Islands (Medium)
- 994. Rotting Oranges (Medium)
- 721. Accounts Merge (Medium)
- 79. Word Search (Medium)
- 310. Minimum Height Trees (Medium)
- 127. Word Ladder (Hard)
733. Flood Fill¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Easy)
-
Tags: array, depth first search, breadth first search, matrix
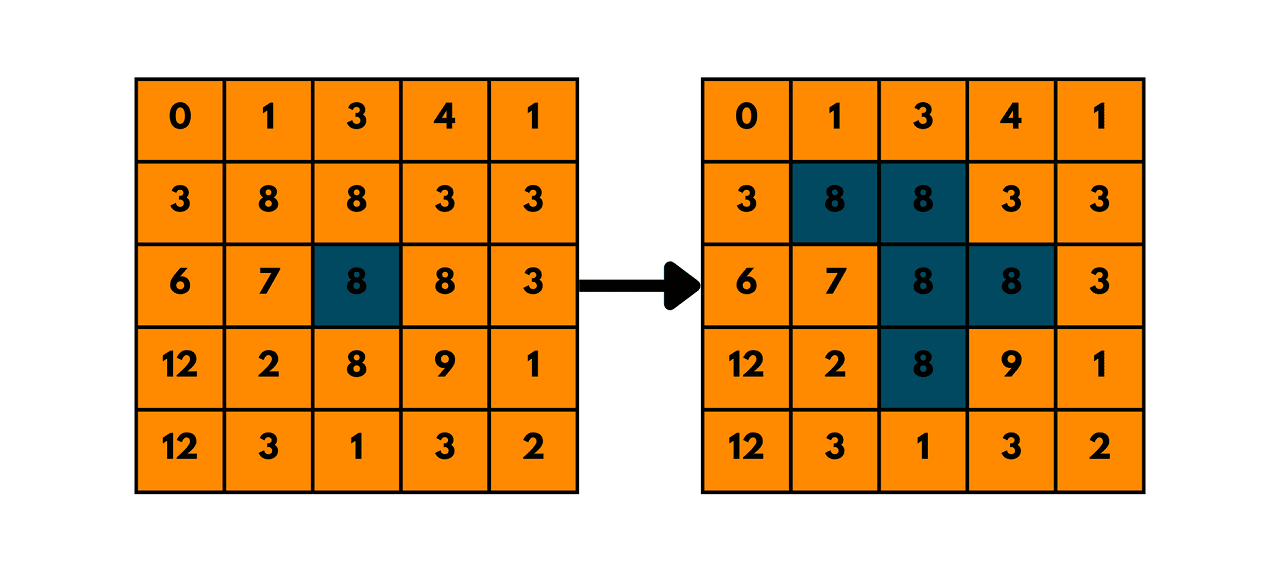
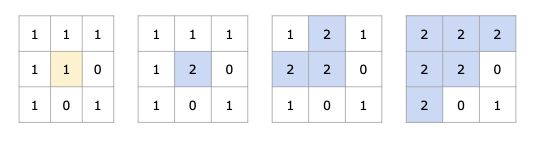
- Replace all the pixels of the same color starting from the given pixel.
- In other words, find the connected component of the starting pixel and change the color of all the pixels in that component.
- Edge cases: If the starting pixel is already the target color, return the image as it is.
- Flood Fill is essentially a graph traversal algorithm (like BFS or DFS) applied to matrices (2D grids). It checks adjacent cells (up, down, left, right) of a starting point to determine whether they belong to the same region. Typically, it involves modifying or marking the cells that belong to the same connected component.
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 |
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# DFS
def floodFillDFS(
image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, color: int
) -> List[List[int]]:
org = image[sr][sc]
m, n = len(image), len(image[0])
if org == color:
return image
def dfs(r, c):
if r < 0 or r >= m or c < 0 or c >= n or image[r][c] != org:
return None
image[r][c] = color
dfs(r - 1, c)
dfs(r + 1, c)
dfs(r, c - 1)
dfs(r, c + 1)
dfs(sr, sc)
return image
# BFS
def floodFillBFS(
image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, color: int
) -> List[List[int]]:
org = image[sr][sc]
m, n = len(image), len(image[0])
dirs = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
if org == color:
return image
q = deque([(sr, sc)])
while q:
r, c = q.popleft()
image[r][c] = color
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and image[nr][nc] == org:
q.append((nr, nc))
return image
image = [[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1]]
sr = 1
sc = 1
print(floodFillDFS(image, sr, sc, 2))
# [[2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 0], [2, 0, 1]]
print(floodFillBFS(image, sr, sc, 2))
# [[2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 0], [2, 0, 1]]
542. 01 Matrix¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, dynamic programming, breadth first search, matrix
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def updateMatrix(mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
dist = [[float("inf")] * n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if mat[i][j] == 0:
dist[i][j] = 0
q.append((i, j))
while q:
r, c = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in directions:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and dist[nr][nc] > dist[r][c] + 1:
dist[nr][nc] = dist[r][c] + 1
q.append((nr, nc))
return dist
mat = [[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]]
print(updateMatrix(mat))
# [[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [1, 2, 1]]
133. Clone Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: hash table, depth first search, breadth first search, graph
from collections import deque
from typing import Optional
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=0, neighbors=None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
# 1. DFS
def cloneGraphDFS(node: Optional["Node"]) -> Optional["Node"]:
if not node:
return None
cloned = {} # {old: new}
def dfs(node):
if node in cloned:
return cloned[node]
new = Node(node.val)
cloned[node] = new
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
new.neighbors.append(dfs(neighbor))
return new
return dfs(node)
# 2. BFS
def cloneGraphBFS(node: Optional["Node"]) -> Optional["Node"]:
if not node:
return None
cloned = {node: Node(node.val)}
q = deque([node])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for neighbor in cur.neighbors:
if neighbor not in cloned:
cloned[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val)
q.append(neighbor)
cloned[cur].neighbors.append(cloned[neighbor])
return cloned[node]
207. Course Schedule¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
- Return true if it is possible to finish all courses, otherwise return false.
- Dependency relationships imply the topological sort algorithm.
- Cycle detection
- Topological Sort
- DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- Time complexity: O(V+E)
- Space complexity: O(V+E)
- Prerequisites: Indegree (Look at the problem 1557. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes)
- Indegree: Number of incoming edges to a vertex
- Applications: task scheduling, course scheduling, build systems, dependency resolution, compiler optimization, etc.
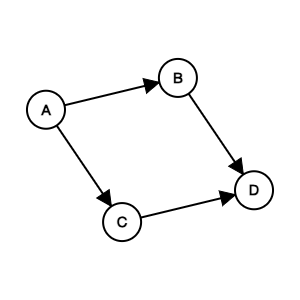
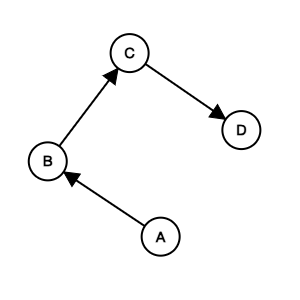
Course to prerequisites mapping
flowchart LR
0((0)) --> 1((1))
0((0)) --> 2((2))
1((1)) --> 3((3))
3((3)) --> 4((4))
1((1)) --> 4((4))Prerequisites to course mapping
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
2((2)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| course | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Initialize
- graph
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| course | [0] |
[0] |
[1] |
[1, 3] |
- in-degree
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[2, 4] - pop
2from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[4] - pop
4from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[3] - pop
3from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[1] - pop
1from the queue
flowchart LR
0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[0] - pop
0from the queue - All courses are taken. Return
True.
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS (Kahn's Algorithm)
def canFinishBFS(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[pre].append(crs)
indegree[crs] += 1
q = deque([i for i in range(numCourses) if indegree[i] == 0])
count = 0
while q:
crs = q.popleft()
count += 1
for nxt in graph[crs]:
indegree[nxt] -= 1
if indegree[nxt] == 0:
q.append(nxt)
return count == numCourses
# DFS + Set
def canFinishDFS1(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
visiting = set()
def dfs(crs):
if crs in visiting: # cycle detected
return False
if graph[crs] == []:
return True
visiting.add(crs)
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
visiting.remove(crs)
graph[crs] = []
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
# DFS + List
def canFinishDFS2(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for pre, crs in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
# 0: init, 1: visiting, 2: visited
status = [0] * numCourses
def dfs(crs):
if status[crs] == 1: # cycle detected
return False
if status[crs] == 2:
return True
status[crs] = 1
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
status[crs] = 2
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
prerequisites = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [3, 4]]
print(canFinishBFS(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS1(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS2(5, prerequisites)) # True
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// BFS
bool canFinishBFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
indegree[pre[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
cnt++;
for (int nxt : graph[cur]) {
indegree[nxt]--;
if (indegree[nxt] == 0) {
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
return cnt == numCourses;
}
// DFS
bool canFinishDFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
}
// 0: not visited, 1: visiting, 2: visited
vector<int> state(numCourses, 0);
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int pre) -> bool {
state[pre] = 1; // visiting
for (int crs : graph[pre]) {
if (state[crs] == 1 || (state[crs] == 0 && dfs(crs))) {
return true;
}
}
state[pre] = 2; // visited
return false;
};
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (state[i] == 0 && dfs(i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Solution sol;
vector<vector<int>> prerequisites = {{1, 0}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3},
{5, 4}, {6, 5}, {7, 6}, {8, 7},
{9, 8}, {10, 9}};
int numCourses = 11;
cout << sol.canFinishBFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
cout << sol.canFinishDFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
return 0;
}
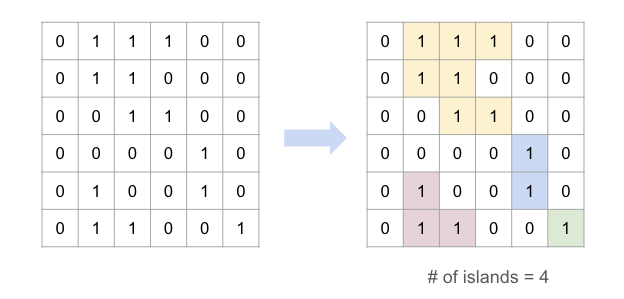
200. Number of Islands¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, matrix
- Count the number of islands in a 2D grid.
- Method 1: DFS
-
Method 2: BFS (use a queue to traverse the grid)
-
How to keep track of visited cells?
- Mark the visited cell as
0(or any other value) to avoid revisiting it. - Use a set to store the visited cells.
- Mark the visited cell as
-
Steps:
- Init: variables
- DFS/BFS: starting from the cell with
1, turn all the connected1s to0. - Traverse the grid, and if the cell is
1, increment the count and call DFS/BFS.
from collections import deque
from copy import deepcopy
from typing import List
# DFS
def numIslandsDFS(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
res = 0
def dfs(r, c):
if r < 0 or r >= m or c < 0 or c >= n or grid[r][c] != "1":
return
grid[r][c] = "2"
dfs(r + 1, c)
dfs(r - 1, c)
dfs(r, c + 1)
dfs(r, c - 1)
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == "1":
dfs(r, c)
res += 1
return res
# BFS + Set
def numIslandsBFS1(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
visited = set()
res = 0
def bfs(r, c):
q = deque([(r, c)])
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = row + dr, col + dc
if (
nr < 0
or nr >= m
or nc < 0
or nc >= n
or grid[nr][nc] == "0"
or (nr, nc) in visited
):
continue
visited.add((nr, nc))
q.append((nr, nc))
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == "1" and (r, c) not in visited:
visited.add((r, c))
bfs(r, c)
res += 1
return res
# BFS + Grid
def numIslandsBFS2(grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]
res = 0
def bfs(r, c):
q = deque([(r, c)])
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = dr + row, dc + col
if (
nr < 0
or nr >= m
or nc < 0
or nc >= n
or grid[nr][nc] != "1"
):
continue
grid[nr][nc] = "2"
q.append((nr, nc))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == "1":
grid[i][j] = "2"
bfs(i, j)
res += 1
return res
grid = [
["1", "1", "1", "1", "0"],
["1", "1", "0", "1", "0"],
["1", "1", "0", "0", "0"],
["0", "0", "0", "0", "0"],
]
print(numIslandsDFS(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
print(numIslandsBFS1(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
print(numIslandsBFS2(deepcopy(grid))) # 1
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
private:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int r, int c)
{
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
if (r < 0 || r >= row || c < 0 || c >= col || grid[r][c] != '1')
{
return;
}
grid[r][c] = '0';
dfs(grid, r - 1, c);
dfs(grid, r + 1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c - 1);
dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1')
{
res++;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> grid = {
{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
{'0', '0', '1', '0', '0'},
{'0', '0', '0', '1', '1'}};
cout << s.numIslands(grid) << endl;
return 0;
}
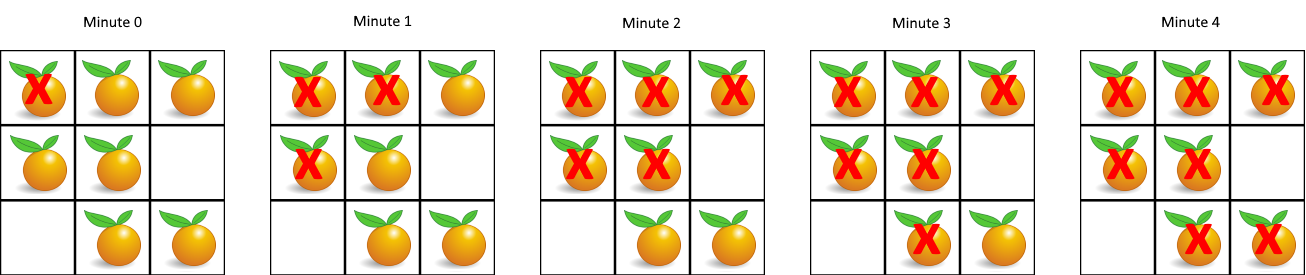
994. Rotting Oranges¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, breadth first search, matrix
- Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange.
- Hint: Multi-source BFS to count the level.
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def orangesRotting(grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
fresh = 0
q = deque()
dirs = [[1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 2:
q.append([i, j])
elif grid[i][j] == 1:
fresh += 1
res = 0
while q and fresh > 0:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
r, c = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in dirs:
nr, nc = dr + r, dc + c
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and grid[nr][nc] == 1:
q.append([nr, nc])
grid[nr][nc] = 2
fresh -= 1
res += 1
return res if fresh == 0 else -1
grid = [[2, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1]]
assert orangesRotting(grid) == 4
721. Accounts Merge¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, hash table, string, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, sorting
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Union Find
def accountsMerge(accounts: List[List[str]]) -> List[List[str]]:
parent = defaultdict(str)
rank = defaultdict(int)
email_to_name = defaultdict(str)
merged_accounts = defaultdict(list)
def find(n):
p = parent[n]
while p != parent[p]:
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]
p = parent[p]
return p
def union(n1, n2):
p1, p2 = find(n1), find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return
if rank[p1] > rank[p2]:
parent[p2] = p1
elif rank[p1] < rank[p2]:
parent[p1] = p2
else:
parent[p2] = p1
rank[p1] += 1
for account in accounts:
name = account[0]
first_email = account[1]
for email in account[1:]:
if email not in parent:
parent[email] = email
rank[email] = 1
email_to_name[email] = name
union(first_email, email)
for email in parent:
root_email = find(email)
merged_accounts[root_email].append(email)
result = []
for root_email, emails in merged_accounts.items():
result.append([email_to_name[root_email]] + sorted(emails))
return result
accounts = [
["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john_newyork@mail.com"],
["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john00@mail.com"],
["Mary", "mary@mail.com"],
["John", "johnnybravo@mail.com"],
]
print(accountsMerge(accounts))
# [['John', 'john00@mail.com', 'john_newyork@mail.com', 'johnsmith@mail.com'],
# ['Mary', 'mary@mail.com'],
# ['John', 'johnnybravo@mail.com']]
79. Word Search¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, string, backtracking, depth first search, matrix
from typing import List
def exist(board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
path = set()
dirs = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
def dfs(r, c, i):
if i == len(word):
return True
if (
r < 0
or r >= m
or c < 0
or c >= n
or board[r][c] != word[i]
or (r, c) in path
):
return False
path.add((r, c))
for dr, dc in dirs:
if dfs(r + dr, c + dc, i + 1):
return True
path.remove((r, c))
return False
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if dfs(i, j, 0):
return True
return False
board = [
["A", "B", "C", "E"],
["S", "F", "C", "S"],
["A", "D", "E", "E"],
]
word = "ABCCED"
print(exist(board, word)) # True
310. Minimum Height Trees¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
from collections import deque
from typing import List
def findMinHeightTrees(n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if n == 1:
return [0]
graph = {i: set() for i in range(n)}
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].add(v)
graph[v].add(u)
q = deque([i for i in range(n) if len(graph[i]) == 1])
remaining = n
while remaining > 2:
size = len(q)
remaining -= size
for _ in range(size):
cur = q.popleft()
nei = graph[cur].pop()
graph[nei].remove(cur)
if len(graph[nei]) == 1:
q.append(nei)
return list(q)
n = 6
edges = [[3, 0], [3, 1], [3, 2], [3, 4], [5, 4]]
print(findMinHeightTrees(n, edges)) # [3, 4]
127. Word Ladder¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: hash table, string, breadth first search
- The most classic BFS problem.
- Return the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, or 0 if no such sequence exists.
- Approach: BFS
- Time Complexity: O(n * m^2)
- Space Complexity: O(n * m)
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS
def ladderLength(beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
n = len(beginWord)
graph = defaultdict(list) # pattern: words
wordList.append(beginWord)
for word in wordList:
for i in range(n):
pattern = word[:i] + "*" + word[i + 1 :]
graph[pattern].append(word)
visited = set([beginWord])
q = deque([beginWord])
res = 1
while q:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
word = q.popleft()
if word == endWord:
return res
for i in range(n):
pattern = word[:i] + "*" + word[i + 1 :]
for neighbor in graph[pattern]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor)
q.append(neighbor)
res += 1
return 0
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"]
print(ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList)) # 5