DFS Basics¶
Table of Contents¶
- 547. Number of Provinces (Medium)
- 1971. Find if Path Exists in Graph (Easy)
- 797. All Paths From Source to Target (Medium)
- 841. Keys and Rooms (Medium)
- 2316. Count Unreachable Pairs of Nodes in an Undirected Graph (Medium)
- 1319. Number of Operations to Make Network Connected (Medium)
- 2492. Minimum Score of a Path Between Two Cities (Medium)
- 3387. Maximize Amount After Two Days of Conversions (Medium)
- 3310. Remove Methods From Project (Medium)
- 2685. Count the Number of Complete Components (Medium)
- 2192. All Ancestors of a Node in a Directed Acyclic Graph (Medium)
- 924. Minimize Malware Spread (Hard)
- 2101. Detonate the Maximum Bombs (Medium)
- 721. Accounts Merge (Medium)
- 207. Course Schedule (Medium)
- 802. Find Eventual Safe States (Medium)
- 928. Minimize Malware Spread II (Hard)
- 2092. Find All People With Secret (Hard)
- 3108. Minimum Cost Walk in Weighted Graph (Hard)
- 261. Graph Valid Tree (Medium) 👑
- 323. Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph (Medium) 👑
547. Number of Provinces¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
- Return the number of provinces.
Union Find¶
- Find by Path Compression
- Union by Rank
- Time Complexity: O(log(n))
- Space Complexity: O(n)
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.par = {i: i for i in range(n)}
self.rank = {i: 1 for i in range(n)}
def find(self, n):
p = self.par[n]
while self.par[p] != p:
self.par[p] = self.par[self.par[p]]
p = self.par[p]
return p
def union(self, n1, n2):
p1, p2 = self.find(n1), self.find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return None
if self.rank[p1] > self.rank[p2]:
self.par[p2] = p1
elif self.rank[p1] < self.rank[p2]:
self.par[p1] = p2
else:
self.par[p2] = p1
self.rank[p1] += 1
def connected(self, n1, n2):
return self.find(n1) == self.find(n2)
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
from template import UnionFind
# DFS (Adjacency Matrix)
def findCircleNumDFSMatrix(isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(isConnected)
visited = set()
def dfs(node):
if node in visited:
return
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in range(n):
if node != neighbor and isConnected[node][neighbor] == 1:
dfs(neighbor)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
dfs(i)
res += 1
return res
# DFS (Adjacency List)
def findCircleNumDFSList(isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
n = len(isConnected)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if isConnected[i][j] == 1:
graph[i].append(j)
graph[j].append(i)
visited = set()
def dfs(node):
if node in visited:
return
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
dfs(neighbor)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
dfs(i)
res += 1
return res
# BFS (Adjacency Matrix)
def findCircleNumBFS(isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(isConnected)
visited = set()
q = deque()
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
res += 1
q.append(i)
while q:
node = q.popleft()
visited.add(node)
for node, val in enumerate(isConnected[node]):
if val == 1 and node not in visited:
q.append(node)
visited.add(node)
return res
# Union Find
def findCircleNumUF(isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(isConnected)
uf = UnionFind(n)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if isConnected[i][j] == 1:
uf.union(i, j)
res = len(set(uf.find(i) for i in range(n)))
return res
# Union Find
def findCircleNum(isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(isConnected)
par = {i: i for i in range(n)}
rank = {i: 0 for i in range(n)}
def find(n):
p = par[n]
while par[p] != p:
par[p] = par[par[p]]
p = par[p]
return p
def union(n1, n2):
p1, p2 = find(n1), find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return None
if rank[p1] > rank[p2]:
par[p2] = p1
elif rank[p1] < rank[p2]:
par[p1] = p2
else:
par[p2] = p1
rank[p1] += 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if isConnected[i][j] == 1:
union(i, j)
res = len(set(find(i) for i in range(n)))
return res
isConnected = [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]
print(findCircleNumDFSList(isConnected)) # 2
print(findCircleNumDFSMatrix(isConnected)) # 2
print(findCircleNumBFS(isConnected)) # 2
print(findCircleNum(isConnected)) # 2
print(findCircleNumUF(isConnected)) # 2
1971. Find if Path Exists in Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Easy)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# DFS (Adjacency List)
def validPathDFS(
n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int
) -> bool:
if not edges and source != destination:
return False
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
visited = set()
def dfs(node):
if node == destination:
return True
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
if dfs(neighbor):
return True
return False
return dfs(source)
n = 3
edges = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 0]]
source = 0
destination = 2
print(validPathDFS(n, edges, source, destination)) # True
797. All Paths From Source to Target¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: backtracking, depth first search, breadth first search, graph
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# DFS (Backtracking)
def allPathsSourceTargetDFS(graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
n = len(graph)
def dfs(node, path):
if node == n - 1:
res.append(path.copy())
return None
for nei in graph[node]:
path.append(nei)
dfs(nei, path)
path.pop()
dfs(0, [0])
return res
# BFS
def allPathsSourceTargetBFS(graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
n = len(graph)
res = []
q = deque([(0, [0])])
while q:
node, path = q.popleft()
if node == n - 1:
res.append(path)
for nei in graph[node]:
q.append((nei, path + [nei]))
return res
graph = [[1, 2], [3], [3], []]
print(allPathsSourceTargetDFS(graph)) # [[0, 1, 3], [0, 2, 3]]
print(allPathsSourceTargetBFS(graph)) # [[0, 1, 3], [0, 2, 3]]
841. Keys and Rooms¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph
from collections import deque
from typing import List
# DFS
def canVisitAllRoomsDFS(rooms: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
n = len(rooms)
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
def dfs(room):
visited[room] = True
for key in rooms[room]:
if not visited[key]:
dfs(key)
dfs(0)
return all(visited)
# BFS
def canVisitAllRoomsBFS(rooms):
n = len(rooms)
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
q = deque([0])
visited[0] = True
while q:
room = q.popleft()
for key in rooms[room]:
if not visited[key]:
visited[key] = True
q.append(key)
return all(visited)
rooms = [[1, 3], [3, 0, 1], [2], [0]]
print(canVisitAllRoomsDFS(rooms)) # False
print(canVisitAllRoomsBFS(rooms)) # False
2316. Count Unreachable Pairs of Nodes in an Undirected Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# DFS (Adjacency List)
def countPairsList1(n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
visited = set()
def dfs(node):
visited.add(node)
size = 1
for nei in graph[node]:
if nei not in visited:
size += dfs(nei)
return size
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
size = dfs(i)
res += size * (n - size)
return res // 2
# DFS(Adjacency List)
def countPairsList2(n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
def dfs(node):
visited[node] = True
size = 1
for nei in graph[node]:
if not visited[nei]:
size += dfs(nei)
return size
res, total = 0, 0
for i in range(n):
if not visited[i]:
size = dfs(i)
res += size * total
total += size
return res
n = 7
edges = [[0, 2], [0, 5], [2, 4], [1, 6], [5, 4]]
print(countPairsList1(n, edges)) # 14
print(countPairsList2(n, edges)) # 14
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
long long countPairs(int n, vector<vector<int>> &edges)
{
unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> graph;
for (const auto &edge : edges)
{
graph[edge[0]].insert(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].insert(edge[0]);
}
unordered_set<int> visited;
function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int node) -> int
{
if (visited.count(node))
{
return 0;
}
visited.insert(node);
int count = 1;
for (const auto &neighbor : graph[node])
{
if (!visited.count(neighbor))
{
count += dfs(neighbor);
}
}
return count;
};
long long res = 0;
long long total = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!visited.count(i))
{
int count = dfs(i);
res += count * (total - count);
}
}
return res / 2;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<int>> edges = {{0, 2}, {0, 5}, {2, 4}, {1, 6}, {5, 4}};
cout << s.countPairs(7, edges) << endl;
return 0;
}
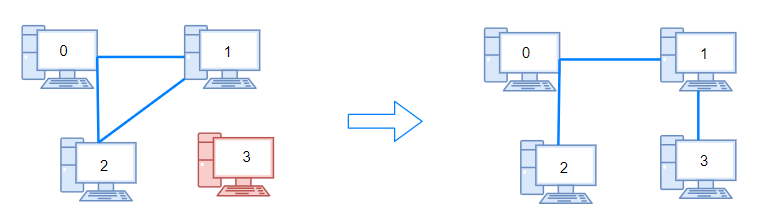
1319. Number of Operations to Make Network Connected¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
- Return the minimum number of operations needed to make all computers connected.
"""
Edge case: If the number of connections is less than n - 1, it is impossible to connect all the computers.
"""
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# DFS
def makeConnectedDFS(n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(connections) < n - 1:
return -1
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in connections:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
visited = set()
component_count = 0
def dfs(node):
for i in graph[node]:
if i not in visited:
visited.add(i)
dfs(i)
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
visited.add(i)
dfs(i)
component_count += 1
return component_count - 1
# BFS
def makeConnectedBFS(n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(connections) < n - 1:
return -1
visited = set()
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in connections:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
def bfs(node):
q = deque([node])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
q.append(nxt)
visited.add(nxt)
component_count = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
visited.add(i)
bfs(i)
component_count += 1
return component_count - 1
n = 4
connections = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 2]]
print(makeConnectedDFS(n, connections)) # 1
print(makeConnectedBFS(n, connections)) # 1
2492. Minimum Score of a Path Between Two Cities¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# DFS
def minScoreDFS(n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in roads:
graph[u].append((v, w))
graph[v].append((u, w))
res = float("inf")
visited = set([1])
def dfs(node):
nonlocal res
for nxt, dist in graph[node]:
res = min(res, dist)
if nxt not in visited:
visited.add(nxt)
dfs(nxt)
dfs(1)
return res
n = 4
roads = [[1, 2, 9], [2, 3, 6], [2, 4, 5], [1, 4, 7]]
print(minScoreDFS(n, roads)) # 5
3387. Maximize Amount After Two Days of Conversions¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, string, depth first search, breadth first search, graph
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# DFS
def maxAmount(
initialCurrency: str,
pairs1: List[List[str]],
rates1: List[float],
pairs2: List[List[str]],
rates2: List[float],
) -> float:
def cal_amount(pairs, rates, initialCurrency):
graph = defaultdict(list)
for (u, v), r in zip(pairs, rates):
graph[u].append((v, r))
graph[v].append((u, 1.0 / r))
amount = {}
def dfs(x, cur):
amount[x] = cur
for to, rate in graph[x]:
if to not in amount:
dfs(to, cur * rate)
dfs(initialCurrency, 1.0)
return amount
day1 = cal_amount(pairs1, rates1, initialCurrency)
day2 = cal_amount(pairs2, rates2, initialCurrency)
return max(day1.get(x, 0.0) / a2 for x, a2 in day2.items())
if __name__ == "__main__":
initialCurrency = "EUR"
pairs1 = [["EUR", "USD"], ["USD", "JPY"]]
rates1 = [2.0, 3.0]
pairs2 = [["JPY", "USD"], ["USD", "CHF"], ["CHF", "EUR"]]
rates2 = [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]
assert maxAmount(initialCurrency, pairs1, rates1, pairs2, rates2) == 720.0
3310. Remove Methods From Project¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph
2685. Count the Number of Complete Components¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
2192. All Ancestors of a Node in a Directed Acyclic Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
924. Minimize Malware Spread¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, hash table, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from typing import List
# Coloring
def minMalwareSpread(graph: List[List[int]], initial: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(graph)
initial = set(initial)
def dfs(x):
visited.add(x)
mark[x] = 1
if x in initial:
v.append(x)
for nxt in range(n):
if graph[x][nxt] and nxt != x and not mark[nxt]:
dfs(nxt)
ans = min(initial)
mx = 0
mark = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
if not mark[i]:
visited = set()
v = []
dfs(i)
if len(v) == 1 and (
len(visited) > mx or len(visited) == mx and v[0] < ans
):
ans, mx = v[0], len(visited)
return ans
graph = [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]
initial = [0, 1]
print(minMalwareSpread(graph, initial)) # 0
2101. Detonate the Maximum Bombs¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, math, depth first search, breadth first search, graph, geometry
721. Accounts Merge¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: array, hash table, string, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, sorting
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Union Find
def accountsMerge(accounts: List[List[str]]) -> List[List[str]]:
parent = defaultdict(str)
rank = defaultdict(int)
email_to_name = defaultdict(str)
merged_accounts = defaultdict(list)
def find(n):
p = parent[n]
while p != parent[p]:
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]
p = parent[p]
return p
def union(n1, n2):
p1, p2 = find(n1), find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return
if rank[p1] > rank[p2]:
parent[p2] = p1
elif rank[p1] < rank[p2]:
parent[p1] = p2
else:
parent[p2] = p1
rank[p1] += 1
for account in accounts:
name = account[0]
first_email = account[1]
for email in account[1:]:
if email not in parent:
parent[email] = email
rank[email] = 1
email_to_name[email] = name
union(first_email, email)
for email in parent:
root_email = find(email)
merged_accounts[root_email].append(email)
result = []
for root_email, emails in merged_accounts.items():
result.append([email_to_name[root_email]] + sorted(emails))
return result
accounts = [
["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john_newyork@mail.com"],
["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john00@mail.com"],
["Mary", "mary@mail.com"],
["John", "johnnybravo@mail.com"],
]
print(accountsMerge(accounts))
# [['John', 'john00@mail.com', 'john_newyork@mail.com', 'johnsmith@mail.com'],
# ['Mary', 'mary@mail.com'],
# ['John', 'johnnybravo@mail.com']]
207. Course Schedule¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
- Return true if it is possible to finish all courses, otherwise return false.
- Dependency relationships imply the topological sort algorithm.
- Cycle detection
- Topological Sort
- DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- Time complexity: O(V+E)
- Space complexity: O(V+E)
- Prerequisites: Indegree (Look at the problem 1557. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes)
- Indegree: Number of incoming edges to a vertex
- Applications: task scheduling, course scheduling, build systems, dependency resolution, compiler optimization, etc.
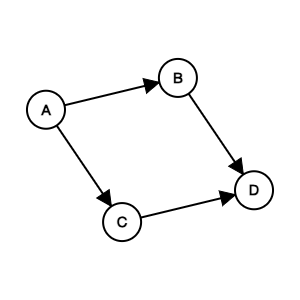
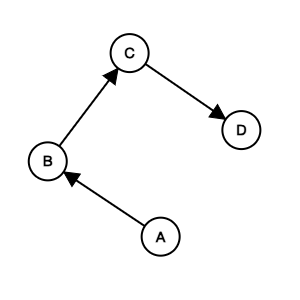
Course to prerequisites mapping
flowchart LR
0((0)) --> 1((1))
0((0)) --> 2((2))
1((1)) --> 3((3))
3((3)) --> 4((4))
1((1)) --> 4((4))Prerequisites to course mapping
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
2((2)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| course | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Initialize
- graph
| prerequisite | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| course | [0] |
[0] |
[1] |
[1, 3] |
- in-degree
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[2, 4] - pop
2from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))
4((4)) --> 3((3))
4((4)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
- queue:
[4] - pop
4from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))
3((3)) --> 1((1))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[3] - pop
3from the queue
flowchart LR
1((1)) --> 0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[1] - pop
1from the queue
flowchart LR
0((0))| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- queue:
[0] - pop
0from the queue - All courses are taken. Return
True.
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# BFS (Kahn's Algorithm)
def canFinishBFS(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[pre].append(crs)
indegree[crs] += 1
q = deque([i for i in range(numCourses) if indegree[i] == 0])
count = 0
while q:
crs = q.popleft()
count += 1
for nxt in graph[crs]:
indegree[nxt] -= 1
if indegree[nxt] == 0:
q.append(nxt)
return count == numCourses
# DFS + Set
def canFinishDFS1(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
visiting = set()
def dfs(crs):
if crs in visiting: # cycle detected
return False
if graph[crs] == []:
return True
visiting.add(crs)
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
visiting.remove(crs)
graph[crs] = []
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
# DFS + List
def canFinishDFS2(numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for pre, crs in prerequisites:
graph[crs].append(pre)
# 0: init, 1: visiting, 2: visited
status = [0] * numCourses
def dfs(crs):
if status[crs] == 1: # cycle detected
return False
if status[crs] == 2:
return True
status[crs] = 1
for pre in graph[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
status[crs] = 2
return True
for crs in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(crs):
return False
return True
prerequisites = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [3, 4]]
print(canFinishBFS(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS1(5, prerequisites)) # True
print(canFinishDFS2(5, prerequisites)) # True
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// BFS
bool canFinishBFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
indegree[pre[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
cnt++;
for (int nxt : graph[cur]) {
indegree[nxt]--;
if (indegree[nxt] == 0) {
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
return cnt == numCourses;
}
// DFS
bool canFinishDFS(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>> &prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
for (auto &pre : prerequisites) {
graph[pre[1]].push_back(pre[0]);
}
// 0: not visited, 1: visiting, 2: visited
vector<int> state(numCourses, 0);
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int pre) -> bool {
state[pre] = 1; // visiting
for (int crs : graph[pre]) {
if (state[crs] == 1 || (state[crs] == 0 && dfs(crs))) {
return true;
}
}
state[pre] = 2; // visited
return false;
};
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (state[i] == 0 && dfs(i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Solution sol;
vector<vector<int>> prerequisites = {{1, 0}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3},
{5, 4}, {6, 5}, {7, 6}, {8, 7},
{9, 8}, {10, 9}};
int numCourses = 11;
cout << sol.canFinishBFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
cout << sol.canFinishDFS(numCourses, prerequisites) << endl;
return 0;
}
802. Find Eventual Safe States¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, graph, topological sort
from collections import defaultdict, deque
from typing import List
# Topological Sort
def eventualSafeNodesTS(graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
n = len(graph)
reverse_graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = [0 for _ in range(n)]
safe = [False for _ in range(n)]
for u in range(n):
for v in graph[u]:
reverse_graph[v].append(u)
indegree[u] = len(graph[u])
q = deque([i for i in range(n) if indegree[i] == 0])
while q:
node = q.popleft()
safe[node] = True
for neighbor in reverse_graph[node]:
indegree[neighbor] -= 1
if indegree[neighbor] == 0:
q.append(neighbor)
return [i for i in range(n) if safe[i]]
# DFS
def eventualSafeNodesDFS(graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
n = len(graph)
state = [0 for _ in range(n)] # 0: unvisited, 1: visiting, 2: visited
def dfs(node):
if state[node] > 0:
return state[node] == 2
state[node] = 1
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if state[neighbor] == 1 or not dfs(neighbor):
return False
state[node] = 2
return True
return [i for i in range(n) if dfs(i)]
graph = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [5], [0], [5], [], []]
print(eventualSafeNodesTS(graph)) # [2, 4, 5, 6]
print(eventualSafeNodesDFS(graph)) # [2, 4, 5, 6]
928. Minimize Malware Spread II¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, hash table, depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
2092. Find All People With Secret¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph, sorting
3108. Minimum Cost Walk in Weighted Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Hard)
-
Tags: array, bit manipulation, union find, graph
261. Graph Valid Tree¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
# Graph
def validTree(n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
if n == 0:
return False
if len(edges) != n - 1:
return False
graph = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
visited = set()
def dfs(node, parent):
if node in visited:
return False
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor != parent and not dfs(neighbor, node):
return False
return True
return dfs(0, -1) and len(visited) == n
print(validTree(5, [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 4]])) # True
print(validTree(5, [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [1, 3], [1, 4]])) # False
323. Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph¶
-
LeetCode | LeetCode CH (Medium)
-
Tags: depth first search, breadth first search, union find, graph
from typing import List
# Union Find
def countComponents(n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
uf = UnionFind(n)
count = n
for u, v in edges:
count -= uf.union(u, v)
return count
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.par = {i: i for i in range(n)}
self.rank = {i: 1 for i in range(n)}
def find(self, n):
p = self.par[n]
while self.par[p] != p:
self.par[p] = self.par[self.par[p]]
p = self.par[p]
return p
def union(self, n1, n2):
p1, p2 = self.find(n1), self.find(n2)
if p1 == p2:
return 0
if self.rank[p1] > self.rank[p2]:
self.par[p2] = p1
elif self.rank[p1] < self.rank[p2]:
self.par[p1] = p2
else:
self.par[p2] = p1
self.rank[p1] += 1
return 1
print(countComponents(5, [[0, 1], [1, 2], [3, 4]])) # 2